 Free UK Delivery On Orders Over £500*
Free UK Delivery On Orders Over £500*
 Free UK Delivery On Orders Over £500*
Free UK Delivery On Orders Over £500*
 Secure Ordering
Secure Ordering
 Up To 5 Year Warranty
Up To 5 Year Warranty
 5* Service & Support
5* Service & Support
What are Lumens?
Lumens are often used to compare the brightness of different light sources. A higher lumen rating means that the light source is producing more light, and therefore is likely to be brighter. For example, a 100-watt incandescent light bulb typically produces around 1600 lumens, while a 60-watt incandescent bulb produces around 800 lumens.
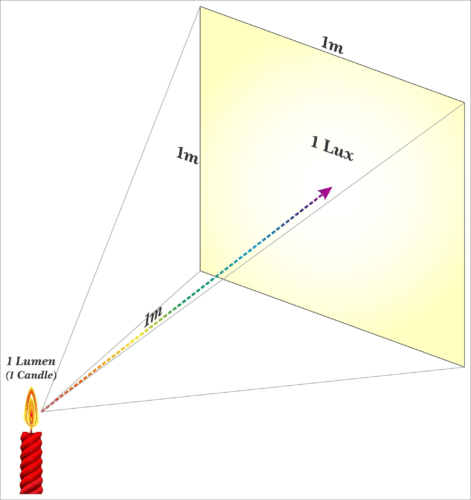
However, it’s important to note that lumens do not take into account the distance of the light source or the area being illuminated. To measure the intensity of light in a specific area or space, you would use the unit lux, which indicates the amount of luminous flux (the total amount of visible light emitted) per unit area. Read more about Lux here.
In general, higher lumen ratings are suitable for tasks that require bright, direct light, such as reading or cooking, while lower lumen ratings may be more appropriate for areas where people will be relaxing or resting.
What light produces the best lumens?
- Type of light source: Different types of light sources produce different amounts of lumens. For example, incandescent bulbs tend to produce fewer lumens per watt than LED bulbs. This means that an LED bulb may produce more lumens than an incandescent bulb using the same amount of power.
- Wattage: The wattage of a light source is a measure of its power consumption. In general, light sources with higher wattages will produce more lumens. However, it’s important to note that the relationship between wattage and lumens is not linear – a higher wattage does not necessarily mean that a light source will produce significantly more lumens.
- Efficiency: The efficiency of a light source refers to how effectively it converts electricity into light. Some light sources are more efficient than others, meaning that they produce more lumens per watt of electricity. For example, LED bulbs are generally more efficient than incandescent bulbs, so they may produce more lumens using the same amount of power.
- Beam angle: The beam angle of a light source indicates the width of the beam of light it produces. A light source with a narrow beam angle will produce a concentrated beam of light that is brighter in the center and fades towards the edges, while a light source with a wide beam angle will produce a more even, diffuse beam of light.
Overall, it’s a good idea to consider all of these factors when selecting a light source that produces high lumens. LED bulbs are generally a good choice, as they tend to be more efficient and have a longer lifespan than other types of light sources. However, it’s also important to consider the specific needs of your application and the desired ambiance when selecting a light source.

What are different types of light source?
There are several types of light sources available, each with its own unique characteristics and uses. Here are a few common types of light sources:
- Incandescent bulbs: Incandescent bulbs are a traditional type of light source that produces light by heating a thin wire filament until it glows. They tend to produce a warm, yellowish light and are relatively inexpensive, but they are also relatively inefficient, as much of the energy they consume is converted into heat rather than light.
- Fluorescent bulbs: Fluorescent bulbs produce light by passing an electrical current through a gas-filled tube, which causes the gas to emit ultraviolet (UV) light. This UV light is then absorbed by a phosphor coating on the inside of the tube, which emits visible light. Fluorescent bulbs tend to be more efficient than incandescent bulbs and have a longer lifespan, but they can also produce a harsh, flickering light.
- LED bulbs: LED (light-emitting diode) bulbs produce light by passing an electrical current through a semiconductor material, which causes it to emit light. LED bulbs are highly efficient and have a long lifespan, but they can also be more expensive than other types of light sources.
- Halogen bulbs: Halogen bulbs are similar to incandescent bulbs, but they contain a small amount of halogen gas in addition to the filament. This causes the filament to burn more brightly and efficiently, resulting in a brighter, whiter light. Halogen bulbs are generally more efficient than incandescent bulbs, but they can also produce a lot of heat.
- Compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs): Compact fluorescent lamps are a type of fluorescent bulb that is designed to fit into a standard light socket. They are more efficient and have a longer lifespan than incandescent bulbs, but they can also produce a harsh, flickering light.
- Light-emitting plasma (LEP) bulbs: Light-emitting plasma bulbs produce light by passing an electrical current through a mixture of gases, which causes the gases to emit light. LEP bulbs are highly efficient and have a long lifespan, but they can be expensive and produce a lot of heat.
There are many other types of light sources available, each with its own unique characteristics and uses. When selecting a light source, it’s important to consider the specific needs of your application and the desired ambiance.

In an LED does a higher wattage mean it is brighter?
The wattage of an LED light bulb is a measure of its power consumption, not its brightness. In general, a higher wattage does not necessarily mean that an LED light bulb will be brighter. Instead, the brightness of an LED light bulb is typically indicated by its lumen output. Lumens (symbol: lm) are a unit of measurement for the amount of light produced by a light source. The higher the lumen rating, the brighter the light source.
So, to determine the brightness of an LED light bulb, you should look at the lumen rating rather than the wattage. For example, a 9-watt LED light bulb with a lumen rating of 800 lumens will be brighter than a 15-watt LED light bulb with a lumen rating of 600 lumens.
It’s also worth noting that the relationship between wattage and lumens is not linear. In other words, a higher wattage does not necessarily mean that an LED light bulb will produce significantly more lumens. Instead, the wattage of an LED light bulb is largely determined by the size and type of LED chips used in the bulb and the overall efficiency of the design.
Overall, when selecting an LED light bulb, it’s important to consider both the wattage and the lumen rating to ensure that you get a light bulb that is both energy-efficient and bright enough for your needs.
How efficient are LEDs?
LEDs (light-emitting diodes) are highly efficient light sources that are capable of converting a large percentage of the energy they consume into visible light. In general, LED bulbs are about 80-90% more efficient than incandescent bulbs, meaning that they produce the same amount of light using significantly less electricity.
There are several factors that contribute to the efficiency of an LED light bulb. One factor is the type and quality of the LED chips used in the bulb. High-quality LED chips are capable of converting a larger percentage of the energy they consume into light, while lower-quality chips are less efficient.
Another factor that affects the efficiency of an LED light bulb is the design of the bulb. A well-designed LED light bulb will have a heat sink and other features to dissipate heat, which helps to improve the overall efficiency of the bulb.
Overall, LED light bulbs are highly efficient and can help reduce energy consumption and lower energy bills. They are also long-lasting, with lifespans that are typically much longer than those of other types of light sources.

What does beam angle on a light mean?
The beam angle of a light refers to the width of the beam of light that is emitted by the light source. It is typically measured in degrees and is a measure of the angle between the two points where the intensity of the light falls to 50% of its maximum value. A light with a narrow beam angle will have a focused beam of light that is concentrated in a specific direction, while a light with a wide beam angle will have a more diffuse beam of light that spreads out over a larger area. The beam angle of a light is an important factor to consider when choosing a light for a specific application, as it determines how the light will behave in different environments and how it will affect the visibility of objects in the area where it is being used.
